Best Fire Resistant Insulation Board: A Comprehensive Guide
In an era where building safety and energy efficiency are paramount, fire resistant insulation boards have emerged as a critical component in construction and renovation. These specialized boards provide a dual function: they significantly enhance a building's thermal performance while offering robust protection against the spread of fire. This comprehensive guide explores the key features, materials, applications, and selection criteria for the best fire resistant insulation boards on the market.

What Are Fire Resistant Insulation Boards?
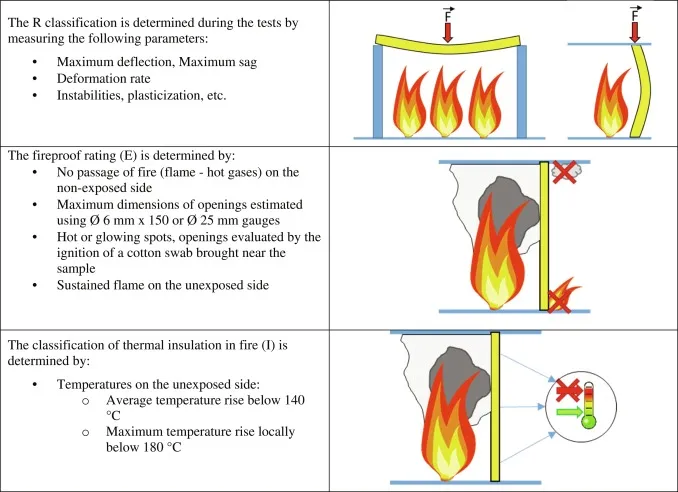
Fire resistant insulation boards are rigid or semi-rigid panels designed to be installed in walls, roofs, floors, and around structural elements. Their primary purpose is to limit heat transfer (insulation) and simultaneously resist ignition, prevent flame spread, and maintain structural integrity for a specified duration during a fire. They are tested and rated according to international fire safety standards, such as ASTM E84 for surface burning characteristics or BS 476 for fire propagation.
Core Materials and Technologies
The effectiveness of a fire resistant insulation board is largely determined by its core material. Each material offers a unique combination of fire performance, insulation value (R-value), and physical properties.
Mineral Wool (Stone Wool or Slag Wool)
Mineral wool boards are manufactured from molten rock or slag spun into fine fibers. They are inherently non-combustible, with melting points exceeding 1000°C. These boards excel in fire resistance, sound absorption, and thermal insulation.
Calcium Silicate Boards
Made from silica sand, lime, and reinforcing fibers, calcium silicate boards are lightweight yet offer exceptional fire resistance and stability at high temperatures. They are often used for fireproofing structural steel and in high-temperature industrial applications.
Vermiculite and Perlite Boards
These boards are created by expanding vermiculite or perlite minerals, which are then bonded with inorganic binders. They provide excellent fire resistance and are known for their lightweight and low thermal conductivity.
Glass Wool with Special Binders
While standard glass wool can melt at high temperatures, specially formulated glass wool boards use high-temperature binders to improve fire resistance, making them suitable for certain fire-rated assemblies.
Key Performance Factors to Consider
Selecting the best board requires evaluating several critical performance metrics beyond just the fire rating.
| Material | Fire Resistance Rating | Typical R-Value per Inch | Key Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral Wool | Excellent (Non-combustible) | R-3.0 - R-4.2 | Superior fire & sound resistance, water repellent | Exterior walls, cavity walls, fire barriers |
| Calcium Silicate | Outstanding (Up to 4-hour ratings) | R-2.0 - R-2.5 | High-temperature stability, dimensionally stable | Structural steel protection, furnaces, high-temp pipelines |
| Vermiculite/Perlite | Excellent (Non-combustible) | R-2.0 - R-2.7 | Lightweight, good for curved surfaces | Fire-rated doors, chimney insulation, industrial |
| Fire-Rated Glass Wool | Good to Very Good | R-3.1 - R-4.3 | Cost-effective, good thermal performance | Residential partitions, attics (where codes allow) |
Primary Applications in Construction
The versatility of fire resistant insulation boards allows them to be used in numerous parts of a building's envelope and structure.
Exterior Wall Systems
Used in rainscreen cladding systems and behind facades, these boards provide continuous insulation and a critical fire break, preventing vertical fire spread in cavity spaces.

Internal Partitions and Walls
They are essential in creating fire-rated walls and partitions that compartmentalize a building, slowing the spread of fire and smoke between rooms or units.
Roof and Floor Assemblies
Fire resistant boards are installed in roof constructions to protect against external fire exposure and in floors to achieve required fire separation and impact insulation ratings.
Structural Fire Protection
Boards like calcium silicate are used to encase structural steel columns and beams, insulating them from heat to prevent premature failure during a fire, which is crucial for overall building stability.
How to Choose the Best Fire Resistant Insulation Board
Pro Tip: Always consult your local building codes and a fire safety engineer before specifying or installing fire resistant insulation. The "best" board is the one that meets the specific fire rating, thermal, and structural requirements of your project.
Consider the following steps:
- Determine the Required Fire Rating: Check building regulations for the necessary fire resistance duration (e.g., 30, 60, 90, 120 minutes) for the specific assembly.
- Assess Thermal Insulation Needs: Calculate the required R-value for energy code compliance and desired energy efficiency.
- Evaluate Environmental Conditions: Consider exposure to moisture, need for vapor permeability, and acoustic performance requirements.
- Review Installation and Handling: Some boards are easier to cut and fit on-site. Consider weight and the need for specialized fasteners or adhesives.
- Verify Certifications: Ensure the product has been tested and certified by recognized bodies (e.g., UL, FM Global, Intertek) for its intended use.
The Future of Fire Resistant Insulation
Innovation continues to drive the market. Trends include the development of hybrid boards that combine different materials for optimized performance, enhanced eco-friendly boards with recycled content, and boards integrated with smart technology for fire monitoring. The push towards sustainable and safer buildings ensures that fire resistant insulation will remain a dynamic and essential field in construction science.
In conclusion, the best fire resistant insulation board is not a one-size-fits-all product. It is a carefully selected system component that balances fire safety, thermal efficiency, durability, and project-specific needs. By understanding the materials, ratings, and applications detailed in this guide, builders, architects, and homeowners can make informed decisions to create safer, more efficient, and more resilient structures.

