Ceramic Composite Dental Materials: Advancements and Applications
Ceramic composite materials have emerged as a cornerstone in modern restorative dentistry, offering an exceptional combination of aesthetics, durability, and biocompatibility. These advanced materials are engineered to mimic the natural appearance and function of tooth structure, making them the preferred choice for a wide range of dental applications, from direct fillings to complex indirect restorations.
Composition and Types of Ceramic Composite Dental Materials
Dental ceramic composites are typically composed of three main components: a ceramic or glass filler material, a resin matrix, and a coupling agent that bonds the filler to the matrix. The specific composition varies depending on the intended application and desired properties.
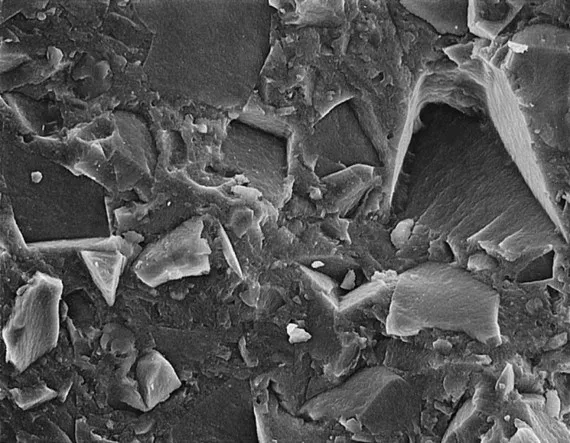 Microscopic view of ceramic composite dental material showing the distribution of ceramic filler particles within the resin matrixbbbb
Microscopic view of ceramic composite dental material showing the distribution of ceramic filler particles within the resin matrixbbbb
Resin Matrix Systems
The resin matrix typically consists of dimethacrylate monomers such as Bis-GMA, UDMA, or TEGDMA. These polymers form the continuous phase that holds the filler particles together and provides the material with its handling characteristics and initial polishability.
Filler Particles
Ceramic filler particles, which can include silica, quartz, or glass ceramics, are incorporated to enhance mechanical properties, reduce polymerization shrinkage, and improve wear resistance. The size, shape, and distribution of these particles significantly influence the material's performance characteristics.
| Filler Type | Particle Size (μm) | Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microfilled | 0.04-0.1 | Excellent polishability, smooth surface finish | Anterior restorations, Class V lesions |
| Hybrid | 0.4-1.0 | Good strength and polishability balance | Universal applications |
| Nanofilled | 0.005-0.02 | Superior aesthetics, high strength | High-stress anterior and posterior restorations |
Advantages of Ceramic Composite Materials in Dentistry
The widespread adoption of ceramic composite materials in dentistry can be attributed to their numerous advantages over traditional restorative materials such as dental amalgam or gold.
Aesthetic Excellence
Ceramic composites can be precisely color-matched to natural tooth structure, making them virtually indistinguishable from surrounding dentition. This aesthetic superiority is particularly important for visible anterior restorations.
Biocompatibility and Safety
Unlike dental amalgam, ceramic composites contain no mercury or other potentially toxic metals. Their excellent biocompatibility minimizes the risk of allergic reactions or adverse tissue responses.
Conservative Tooth Preparation
The adhesive bonding capability of ceramic composites allows for more conservative tooth preparations, preserving healthy tooth structure compared to traditional restorations that require mechanical retention.
oooo bbbbDental procedure demonstrating the adhesive bonding technique used for ceramic composite restorationsbbbb
bbbbDental procedure demonstrating the adhesive bonding technique used for ceramic composite restorationsbbbb
Clinical Applications and Techniques
Ceramic composite materials are versatile and can be used in various clinical scenarios, each requiring specific material selection and application techniques.
Direct Restorations
For direct restorations, the material is placed incrementally and light-cured directly in the prepared cavity. Proper isolation, adhesive application, and curing protocols are critical for long-term success.
Indirect Restorations
CAD/CAM technology has expanded the applications of ceramic composites to include inlays, onlays, and even crowns. These restorations are fabricated extraorally and then cemented to the prepared teeth.
| Application Type | Material Variants | Expected Longevity | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I-IV Cavities | Universal composites, flowable composites | 7-12 years | Incremental placement, proper curing |
| Veneers | Microfilled, nanofilled composites | 5-10 years | Color matching, surface characterization |
| CAD/CAM Restorations | High-density ceramic composites | 10-15 years | Precise fit, adhesive cementation |
Recent Advancements and Future Directions
The field of ceramic composite dental materials continues to evolve, with research focusing on improving mechanical properties, simplifying clinical procedures, and enhancing long-term performance.
Smart Composites
Emerging technologies include "smart" composites with bioactive properties that can release fluoride or calcium phosphate ions to help prevent secondary caries and promote remineralization of adjacent tooth structure.
Bulk-Fill Composites
Recent developments in bulk-fill composites allow for placement in 4-5mm increments, reducing chair time and potential errors associated with traditional incremental techniques.
3D Printing Applications
The advent of 3D printing technologies has opened new possibilities for fabricating ceramic composite restorations with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
oooo bbbbAdvanced ceramic composite materials shown alongside digital dentistry technologies representing future directionsbbbb
bbbbAdvanced ceramic composite materials shown alongside digital dentistry technologies representing future directionsbbbb
Conclusion
Ceramic composite dental materials represent a significant advancement in restorative dentistry, offering an ideal combination of aesthetic appeal, functional performance, and biological compatibility. As research continues to address challenges such as polymerization shrinkage and wear resistance, these materials are poised to become even more integral to modern dental practice. The ongoing development of novel formulations and application techniques ensures that ceramic composites will continue to play a vital role in providing patients with durable, natural-looking restorations that promote oral health and wellbeing.

