The Role of Optical Coating Materials in Virtual Reality Systems
Virtual Reality (VR) technology has evolved from a niche concept to a mainstream platform for entertainment, education, and professional training. At the heart of this immersive experience lies optical engineering, where the quality of visual output is paramount. While lenses, displays, and sensors often receive significant attention, the unsung heroes enabling high-fidelity VR are advanced optical coating materials. These specialized thin-film coatings are applied to optical components to manipulate light behavior, directly impacting clarity, comfort, and the overall realism of the virtual world.
Fundamental Functions of Optical Coatings in VR Optics
Optical coatings are nanoscale layers of materials deposited on surfaces like lenses and beam splitters. In VR systems, which primarily rely on complex lens assemblies placed close to the user's eyes, these coatings perform several non-negotiable functions.
Anti-Reflective (AR) Coatings
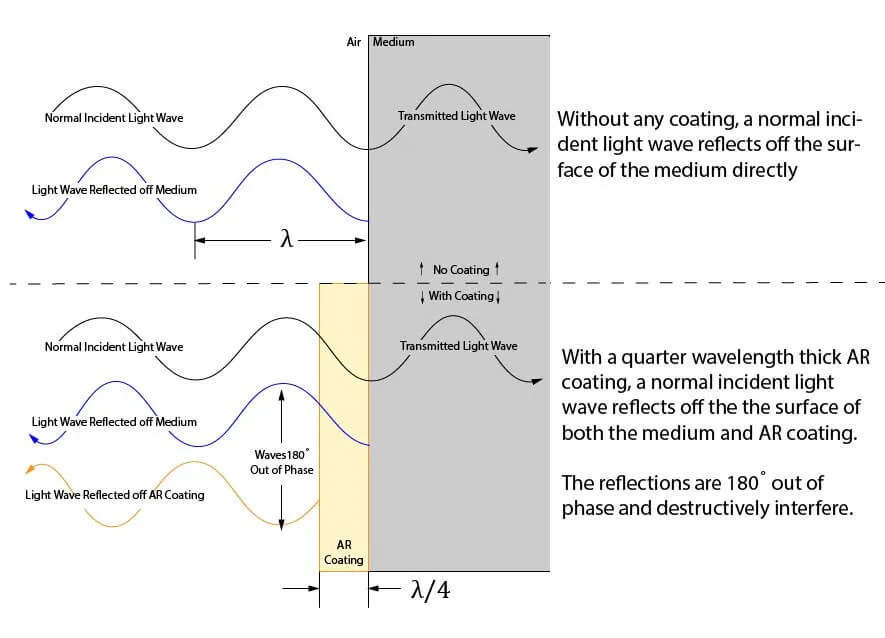
The most crucial coating for VR is the anti-reflective (AR) coating. VR lenses have multiple air-glass surfaces where internal reflections can cause ghost images, glare, and a significant reduction in contrast. AR coatings, often composed of alternating layers of materials like magnesium fluoride (MgF₂) and titanium dioxide (TiO₂), minimize these reflections by causing destructive interference of reflected light waves. This maximizes light transmission from the micro-display to the user's eye, resulting in a brighter, sharper image with deeper blacks.
High-Reflective and Dichroic Coatings
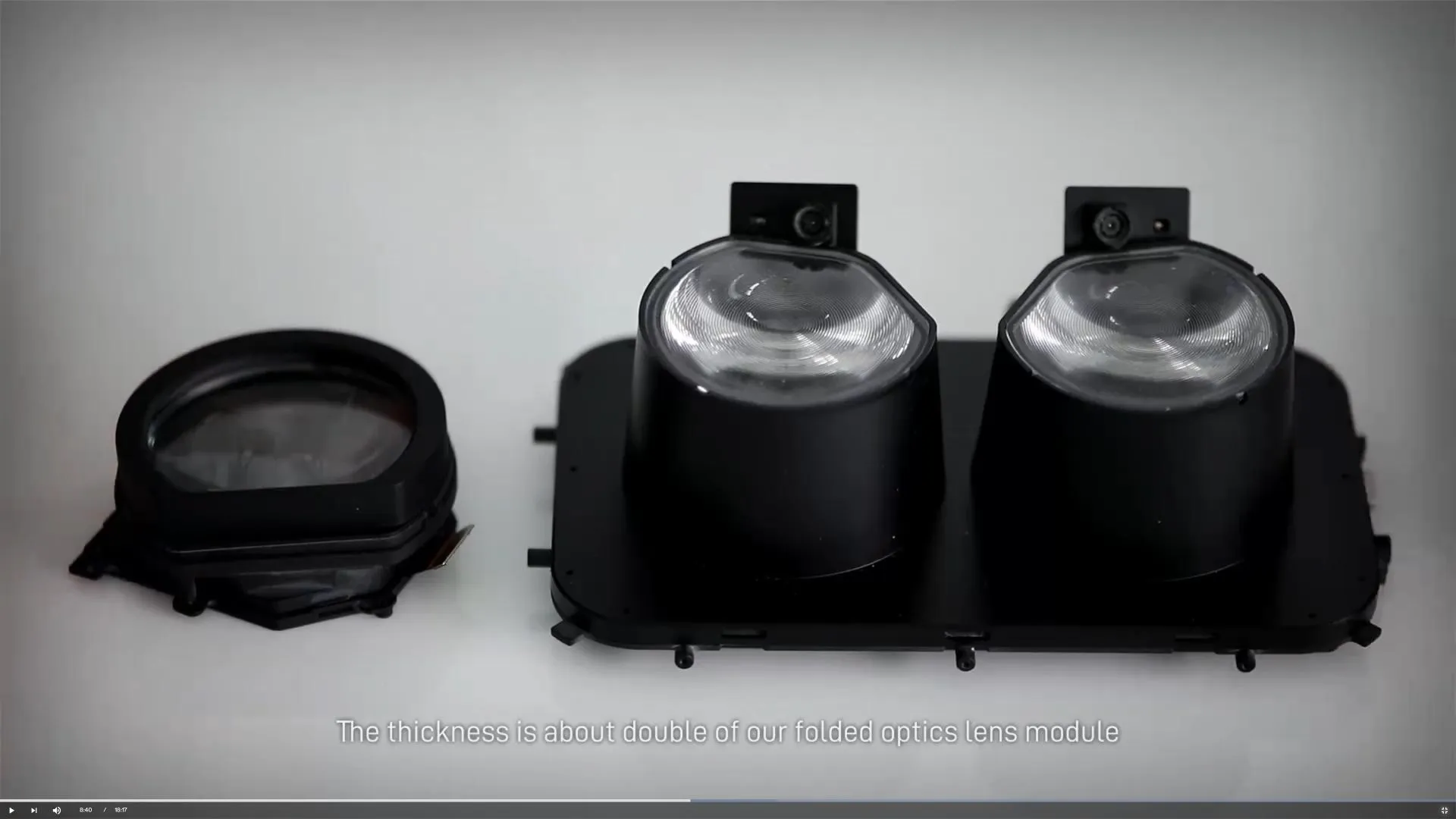
For VR systems using pancake lenses or complex folded optical paths to reduce device size, highly reflective mirrors are essential. Metallic coatings (e.g., aluminum, silver) and more advanced dielectric dichroic coatings are used. Dichroic coatings can be engineered to reflect specific wavelengths (like RGB from displays) while transmitting others, enabling precise color management and optical path folding within a compact headset.
Durable and Oleophobic Coatings
Given the proximity to the user, VR lenses are susceptible to scratches, moisture, and skin oils. A hard, durable coating (often a diamond-like carbon film) protects the underlying optical material. An oleophobic top layer repels fingerprints and smudges, ensuring consistent optical performance and ease of maintenance.
Impact on Key VR Performance Metrics
The application of these coatings directly correlates with measurable improvements in user experience.
| Performance Metric | Challenge Without Coatings | Solution with Optical Coatings | Result for User |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Efficiency & Brightness | Up to 8-10% light loss per uncoated surface; dim image. | AR coatings achieve >99.5% transmission per surface. | Brighter display, lower power consumption for same perceived brightness. |
| Contrast & Image Fidelity | Internal reflections create "ghosting" and haze, reducing contrast. | AR and absorption coatings suppress stray light. | Sharper images, deeper blacks, more realistic and immersive scenes. |
| Color Accuracy & Uniformity | Lens materials can cause chromatic aberrations and color shifts. | Dichroic and corrective coatings tune wavelength transmission. | True-to-life colors and consistent color across the entire field of view. |
| Form Factor & Weight | Simple optics require long physical paths, making headsets bulky. | High-reflectivity coatings enable folded optics (pancake lenses). | Slimmer, lighter, and more comfortable headset designs. |

Advanced Coating Technologies Shaping Next-Generation VR
As VR pushes towards varifocal displays (simulating depth of focus) and augmented reality (AR) integration, coating demands become more sophisticated.
Electrochromic and Tunable Coatings
Research is ongoing into coatings that can change their optical properties (transmission, reflection) electronically. In a varifocal system, such a coating could dynamically adjust to control light paths or intensity for different focal planes, enhancing visual comfort and reducing vergence-accommodation conflict.
Broadband and Wide-Angle AR Coatings
Ultra-wide field-of-view (FOV) headsets require coatings that perform consistently at extreme angles of incidence. New multilayer designs using materials with varying refractive indices are being developed to prevent color fringing and reflection across the entire FOV.
Nanostructured and Metamaterial Coatings
Beyond traditional thin films, sub-wavelength nanostructures and optical metamaterials offer unprecedented control over light. These can create ultra-efficient AR surfaces, polarizers, and spectral filters that are thinner and more effective than conventional coatings, paving the way for even more compact and capable optical engines.
Conclusion: An Indispensable Enabling Technology
Optical coating materials are not merely an accessory but a foundational technology for high-performance Virtual Reality. They solve critical problems of light loss, glare, and physical bulk that would otherwise severely limit visual quality and user comfort. From enabling the sleek form factors of modern headsets to ensuring the vivid, crisp images that define immersion, these advanced thin films are integral to the VR experience. As the industry strives for photorealistic graphics, wider fields of view, and all-day wearability, continued innovation in optical coating materials—spanning new deposition techniques, novel materials, and intelligent designs—will remain at the forefront of VR hardware advancement.

